publications
2025
-
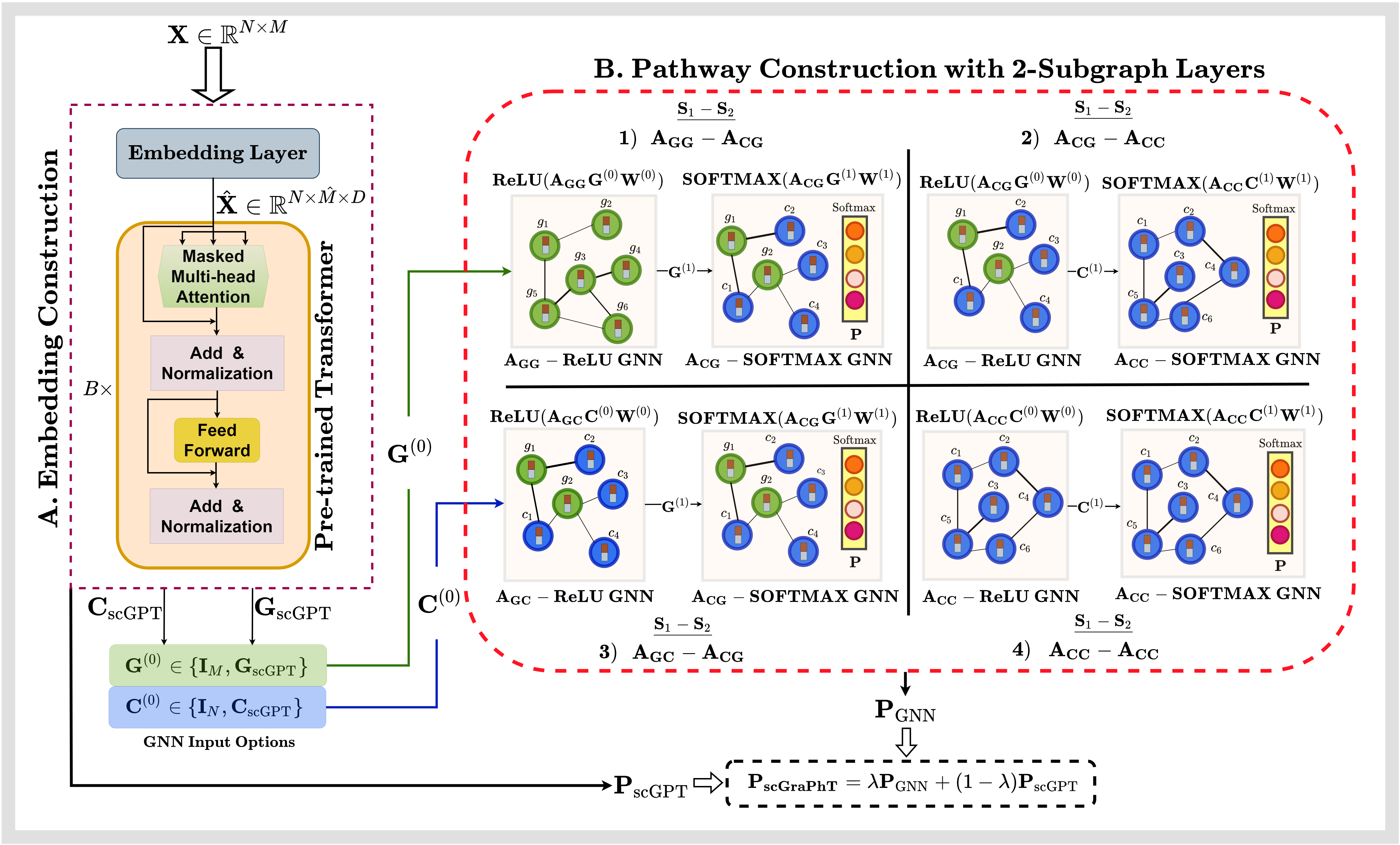 scGraPhT: Merging Transformers and Graph Neural Networks for Single-Cell AnnotationEmirhan Koç and others.IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2025
scGraPhT: Merging Transformers and Graph Neural Networks for Single-Cell AnnotationEmirhan Koç and others.IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2025Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a powerful technique for understanding cellular heterogeneity. However, the high dimensionality and sparsity of scRNA-seq data pose significant challenges for accurate cell type annotation. In this paper, we introduce scGraPhT, a novel framework that combines the strengths of transformers and graph neural networks (GNNs) to enhance single-cell annotation. The proposed method constructs a graph representation of single-cell data, where nodes represent cells and edges capture relationships based on gene expression similarity. A transformer-based architecture is then employed to learn rich representations of these graphs, enabling effective cell type classification. Experimental results demonstrate that scGraPhT outperforms existing methods in terms of accuracy and robustness across various datasets. Our approach provides a promising direction for improving single-cell analysis through advanced graph-based techniques.
@article{koc2025scgraph, author = {Koç, Emirhan and others.}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks}, title = {scGraPhT: Merging Transformers and Graph Neural Networks for Single-Cell Annotation}, year = {2025}, volume = {11}, number = {}, pages = {505-519}, doi = {10.1109/TSIPN.2025.3573591} } -
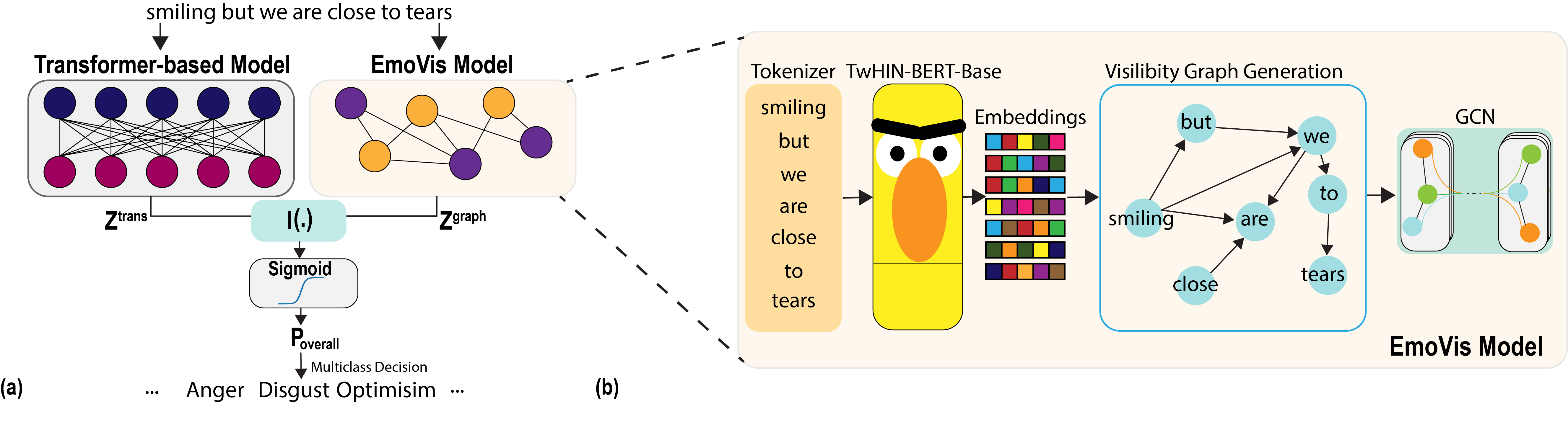 Emotion Classification With Visibility GraphsEcem Şimşek, Atakan Topcu*, Emirhan Koç*, and 2 more authorsIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2025
Emotion Classification With Visibility GraphsEcem Şimşek, Atakan Topcu*, Emirhan Koç*, and 2 more authorsIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2025This paper presents a novel approach for emotion classification using visibility graphs. The proposed method constructs visibility graphs from time series data, capturing the underlying structure of the data. By analyzing the topological features of these graphs, we can effectively classify emotions. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving high accuracy in emotion classification tasks. The proposed method provides a promising direction for emotion recognition in various applications, including human-computer interaction and affective computing.
@article{simsek2025emotion, author = {Şimşek, Ecem and Topcu, Atakan and Koç, Emirhan and Saritas, Emine Ulku and Koç, Aykut}, journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters}, title = {Emotion Classification With Visibility Graphs}, year = {2025}, volume = {32}, number = {}, pages = {2055-2059}, doi = {10.1109/LSP.2025.3567033} }
2024
-
 Trainable Fractional Fourier TransformEmirhan Koç, Tuna Alikaşifoğlu, Arda Can Aras, and 1 more authorIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024
Trainable Fractional Fourier TransformEmirhan Koç, Tuna Alikaşifoğlu, Arda Can Aras, and 1 more authorIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024This paper introduces a trainable fractional Fourier transform (TFRFT) that learns the optimal fractional order for a given signal. The TFRFT is formulated as a neural network layer, enabling end-to-end training with backpropagation. Experimental results demonstrate that the TFRFT can adaptively learn the best fractional order, outperforming traditional fixed-order fractional Fourier transforms in various signal processing tasks. The proposed method provides a flexible and efficient approach for analyzing signals in the fractional Fourier domain.
@article{koc2024trainable, author = {Koç, Emirhan and Alikaşifoğlu, Tuna and Aras, Arda Can and Koç, Aykut}, journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters}, title = {Trainable Fractional Fourier Transform}, year = {2024}, volume = {31}, number = {}, pages = {751-755}, doi = {10.1109/LSP.2024.3372779} } -
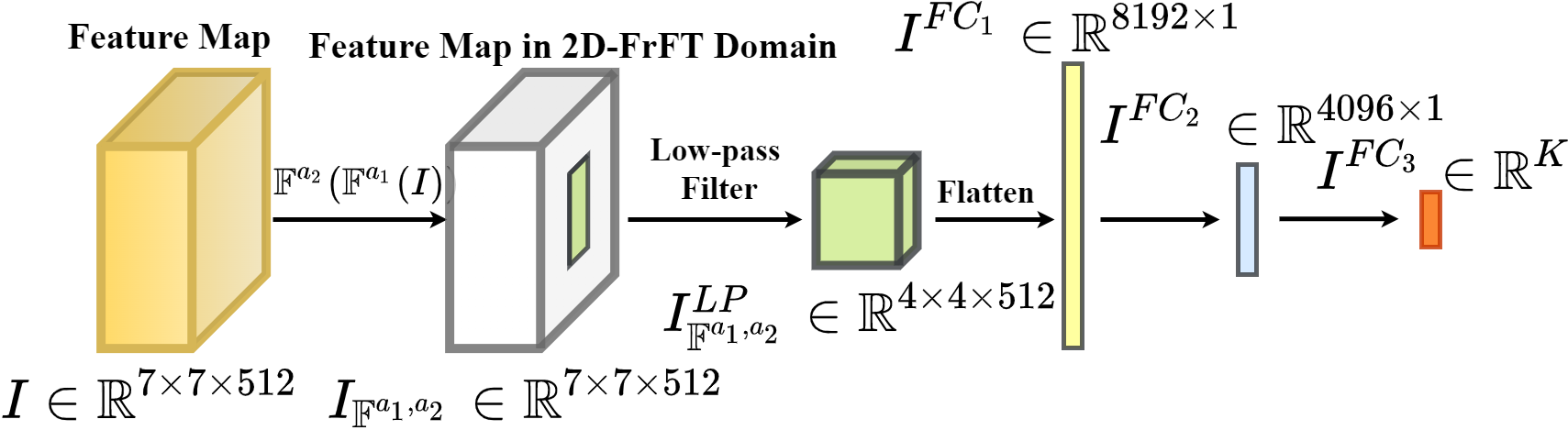
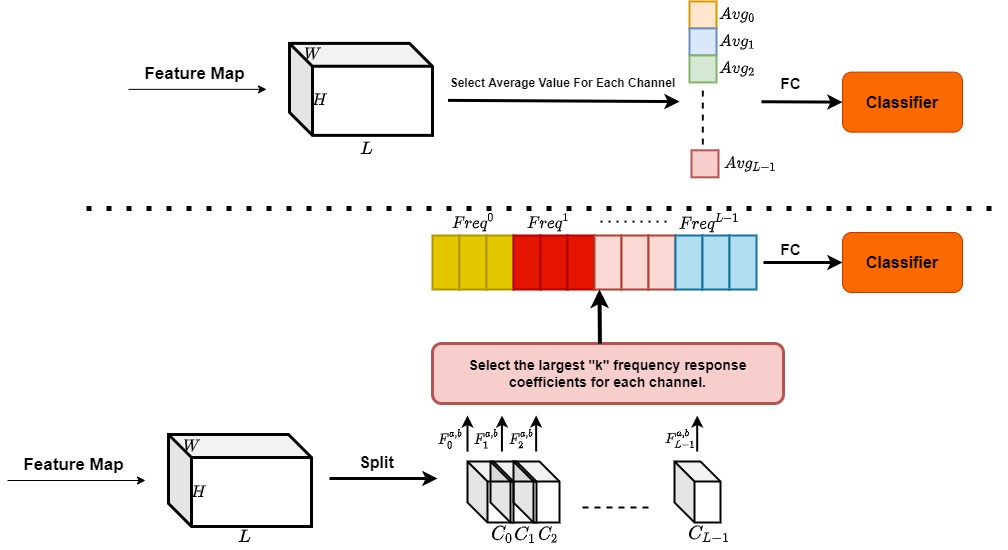 Maximally Selective Fractional Fourier PoolingEmirhan Koç, Yunus Emre Ekiz, Haldun Özaktaş, and 1 more authorIn 2024 32nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 2024
Maximally Selective Fractional Fourier PoolingEmirhan Koç, Yunus Emre Ekiz, Haldun Özaktaş, and 1 more authorIn 2024 32nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 2024This paper introduces a novel pooling method called Maximally Selective Fractional Fourier Pooling (MSFRP) for deep learning applications. MSFRP combines the principles of fractional Fourier transforms with a selective pooling strategy to enhance feature extraction in convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The proposed method adaptively selects the most informative features from the fractional Fourier domain, improving the model’s performance in various tasks such as image classification and object detection. Experimental results demonstrate that MSFRP outperforms traditional pooling methods, achieving higher accuracy and robustness across multiple datasets. The findings highlight the potential of fractional Fourier transforms in enhancing deep learning architectures.
@inproceedings{10600916, author = {Koç, Emirhan and Ekiz, Yunus Emre and Özaktaş, Haldun and Koç, Aykut}, booktitle = {2024 32nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU)}, title = {Maximally Selective Fractional Fourier Pooling}, year = {2024}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1-4}, doi = {10.1109/SIU61531.2024.10600916} }
2022
-
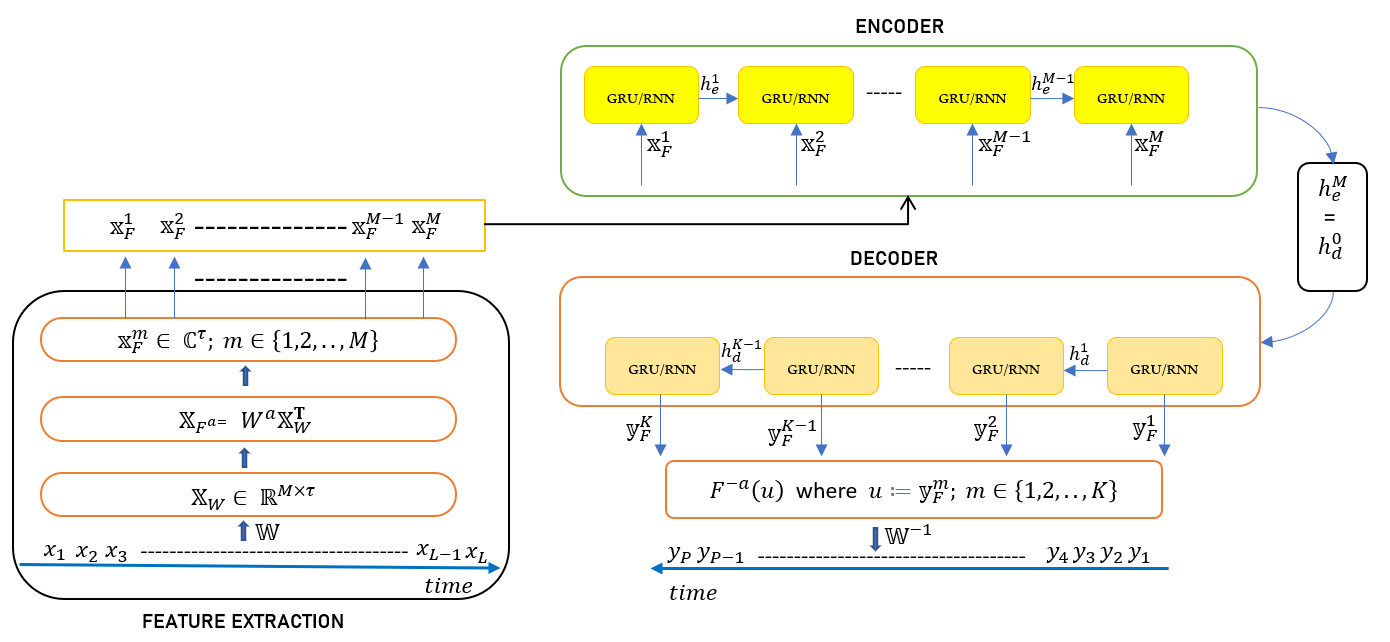 Fractional Fourier Transform in Time Series PredictionEmirhan Koç and Aykut KoçIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022
Fractional Fourier Transform in Time Series PredictionEmirhan Koç and Aykut KoçIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022This paper investigates the application of the fractional Fourier transform (FRFT) in time series prediction. The FRFT is a generalization of the classical Fourier transform, allowing for the analysis of signals in a fractional domain. We propose a novel approach that combines the FRFT with machine learning techniques to enhance time series forecasting accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms traditional Fourier-based approaches, achieving significant improvements in prediction performance across various datasets. The findings highlight the potential of the FRFT as a powerful tool for time series analysis and forecasting.
@article{koc2022fractional, author = {Koç, Emirhan and Koç, Aykut}, journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters}, title = {Fractional Fourier Transform in Time Series Prediction}, year = {2022}, volume = {29}, number = {}, pages = {2542-2546}, doi = {10.1109/LSP.2022.3228131} } -
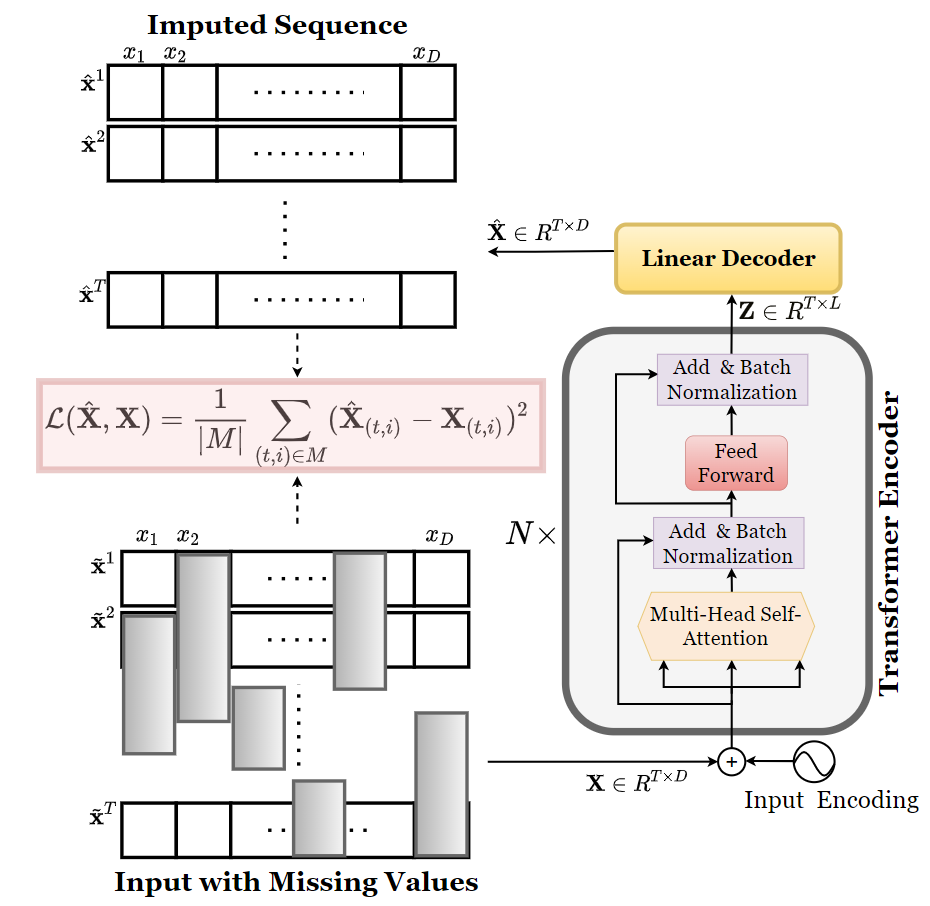 Multivariate Time Series Imputation With TransformersA. Yarkın Yıldız, Emirhan Koç, and Aykut KoçIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022
Multivariate Time Series Imputation With TransformersA. Yarkın Yıldız, Emirhan Koç, and Aykut KoçIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022This paper presents a novel approach for multivariate time series imputation using transformers. The proposed method leverages the self-attention mechanism of transformers to capture complex dependencies among multiple time series variables. By modeling the temporal relationships and interactions between variables, the transformer-based imputation framework effectively fills in missing values in multivariate time series data. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms traditional imputation techniques, achieving higher accuracy and robustness in various datasets. The findings highlight the potential of transformers for addressing missing data challenges in multivariate time series analysis.
@article{yildiz2022multivariate, author = {Yıldız, A. Yarkın and Koç, Emirhan and Koç, Aykut}, journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters}, title = {Multivariate Time Series Imputation With Transformers}, year = {2022}, volume = {29}, number = {}, pages = {2517-2521}, doi = {10.1109/LSP.2022.3224880} }